Economic indicators definition
Economic indicators are statistical measures that help policymakers and economists evaluate the state of the economy and forecast future developments.
Economic indicators measure the performance and health of an economy. Policymakers and economists use this economic data to assess current conditions and predict future trends. Common economic indicators include gross domestic product (GDP), unemployment rates, inflation, and consumer spending.
Classifying economic indicators
Economic indicators are divided into three categories:
- Leading indicators: these predict future economic activity
- Lagging indicators: measure trends after they occur
- Coincident indicators: fluctuate as the overall economy moves
Economic indicators examples
Here are some of the most common economic indicators, grouped by type.
Leading economic indicators
- Consumer confidence index: measures how optimistic consumers are about the economy.
- Stock market performance: reflects investor sentiment and expectations.
- Building permits: indicates future construction activity.
- Manufacturers' new orders: suggests future production volume.
- Average Weekly Hours (Manufacturing): longer hours often signal upcoming growth.
Lagging economic indicators
- Unemployment rate: measures the percentage of the labor force that is jobless and actively seeking work.
- Corporate profits: reflects past economic activity and business performance.
- Labor cost per unit of output: indicates changes in wage pressures and productivity.
- Outstanding loans to businesses and consumers: tracks borrowing activity after economic shifts.
Coincident economic indicators
Gross Domestic Product (GDP): measures the total value of goods and services produced.
Industrial production: tracks the output of factories, mines, and utilities.
Personal income: indicates household earning power.
Retail sales: shows consumer spending trends.
Nonfarm payrolls: tracks job growth across most sectors.
Other widely watched economic indicators
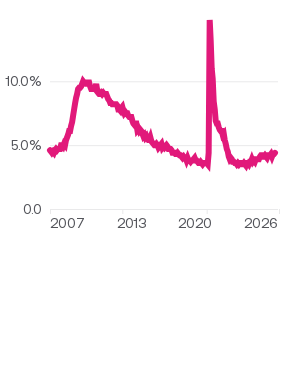
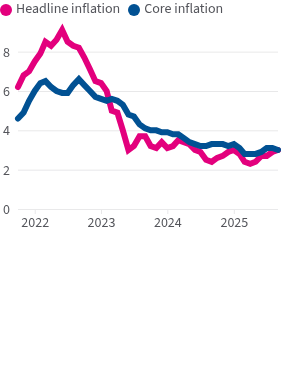
- Inflation rate: shows changes in the cost of goods and services, and is typically tracked by the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and Producer Price Index (PPI).
- Interest rates: interest rates (the fees a lender charges for borrowing money) fluctuate according to the federal funds rate and influence borrowing, spending, and investment.
- Housing starts: measures the amount of new residential construction beginning.
- Trade balance: the difference between a nation’s exports and imports.
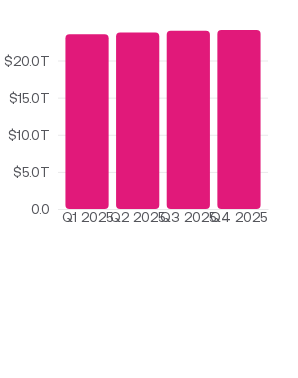
- Money supply: reflects the amount of liquid money circulating in the economy. In the United States, this is primarily measured as a combination of M1 (currency in circulation) and M2 (M1 plus longer-term savings deposits).
- Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI): gauges business conditions in the manufacturing and services sectors.